Is Intermittent Fasting effective for fat loss?
Is Intermittent Fasting effective for fat loss?
The short answer is yes.
Intermittent fasting, or IF, is a form of time restrictive easting which has been shown to promote fat loss (Welton et al., 2020).
How does it work?
IF works by reducing the number of calories you eat in any given time period – usually measured over a 24hr cycle. One of the most common forms is restricting eating to a 6-8 hour window each day.
Why does it work?
IF works by providing a method of calorie restriction.
Is it the best way to reduce calories?
IF may work for you, but it’s not the only, or even the most effective, way to reduce calorie intake to reduce excess fat mass (Rynders et al., 2019).
To lose fat a calorie deficit is required and IF can be used to create a calorie deficit, but IF has not been shown to produce better results than other calorie deficit approaches to fat loss.
IF may not be optimal for muslce gains.
During a calorie deficit the main aim is to reduce fat mass. A secondary goal is to preserve lean mass as much as possible. IF restricts calories and similarly to other dietary restriction protocols IF may not be the optimal way to retain lean mass (muscle) (Williamson & Moore, 2021).
Cominbing IF with HIIT?
A recent study has deomstrated that combining IF with HIIT may improve lean mass while reducing fat mass (Batitucci et al., 2022). Other systematic reviews appear to support the use of IF with HIIT to promote fat loss and retain lean mass (Sandoval et al., 2021).
The best way to implement IF and HITT?
If IF is something you want to try my recommendations are to ensure that you are consuming adequate protein in your diet and including resistance training in your weekly exercise program.
How do I know if I’m losing fat or lean mass?
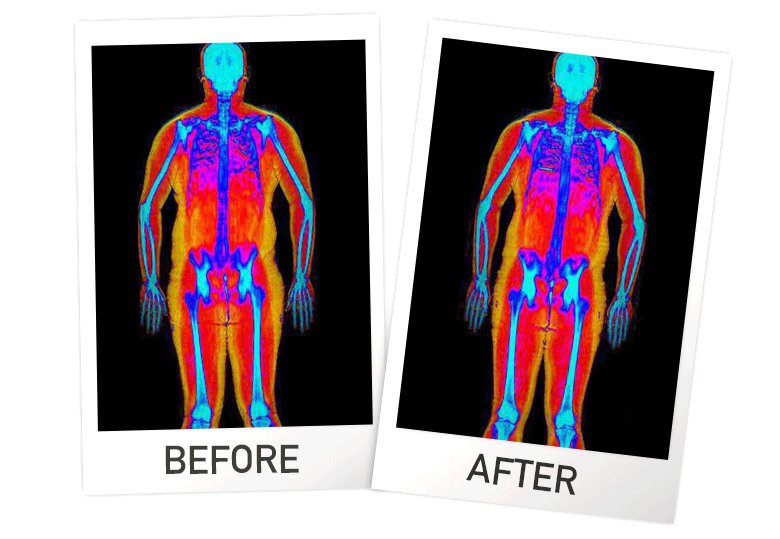
A DEXA will be able to track changes in fat mass and lean mass to make sure your diet strategy and workouts are optimising your body composition!
BRENDAN BARRY (AEP, AES, ESSAM)
References
Batitucci, G., Faria Junior, E. V., Nogueira, J. E., Brandão, C. F. C., Abud, G. F., Ortiz, G. U., . . . Freitas, E. C. (2022). Impact of Intermittent Fasting Combined With High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition, Metabolic Biomarkers, and Physical Fitness in Women With Obesity. Frontiers in nutrition, 9, 884305-884305. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.884305
Rynders, C. A., Thomas, E. A., Zaman, A., Pan, Z., Catenacci, V. A., & Melanson, E. L. (2019). Effectiveness of Intermittent Fasting and Time-Restricted Feeding Compared to Continuous Energy Restriction for Weight Loss. Nutrients, 11(10), 2442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102442
Sandoval, C., Santibañez, S., & Villagrán, F. (2021). Effectiveness of intermittent fasting to potentiate weight loss or muscle gains in humans younger than 60 years old: a systematic review. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 72(6), 734-745. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2020.1868412
Welton, S., Minty, R., O’Driscoll, T., Willms, H., Poirier, D., Madden, S., & Kelly, L. (2020). Intermittent fasting and weight loss: Systematic review. Can Fam Physician, 66(2), 117-125.
Williamson, E., & Moore, D. R. (2021). A Muscle-Centric Perspective on Intermittent Fasting: A Suboptimal Dietary Strategy for Supporting Muscle Protein Remodeling and Muscle Mass? [Perspective]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8.